In this guide you will stream health data from Sahha to Supabase Postgres using Sahha Webhooks and Supabase Edge Functions (TypeScript/Deno) — choosing which data types to send, verifying webhooks securely, and persisting structured events in a Postgres table.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure you have:
- Node.js 18+ installed
- A Supabase project created
- Supabase CLI installed:
npm i supabase --save-dev - Docker Desktop running (required for Edge Functions local dev)
- Access to Data Delivery → Webhooks in the Sahha dashboard
Get data flowing into Sahha Required
Webhooks only fire when Sahha is actually receiving data. Choose how to connect:
Use the Sahha Demo App (fastest way to test)
- In the Sahha dashboard, go to Configure → Demo App
- Copy the Configuration URL (or scan the QR code)
- Install the Sahha Demo App from the App Store / Google Play
- In the demo app, paste the Configuration URL (or scan the QR) to connect it to your project
- Keep the demo app running so it can collect and submit device data
Once connected, you should see a new profile appear in your Sahha project and data beginning to flow.
If you’ve already integrated the Sahha SDK into your application, ensure that:
- Your app is successfully streaming data to Sahha
- You are setting a stable
externalIdwhen creating Sahha profiles (for example, your Supabase Auth UID)
This externalId will later be sent back in webhooks as X-External-Id, which allows you to map Sahha events to the correct user in your database.
Set up your Supabase Edge Functions project
Install the Supabase CLI (once per machine)
npm i supabase --save-devLog in to Supabase
npx supabase loginThis links your local machine to your Supabase account.
Download the starter project — it includes an Edge Function with signature verification, Postgres migrations, and all project configuration already set up.
Download starter projectAfter downloading:
- Unzip and open the project
- Link it to your Supabase project using your Project ID (found in Supabase Dashboard → Project Settings → General):
cd sahha-supabase-webhooks-starter
npx supabase link --project-ref your-project-id- Apply the database migration to create the
sahha_eventstable:
npx supabase db pushWhen prompted, confirm with Y to apply the migration. You can verify the table was created in the Supabase Dashboard → Table Editor → sahha_events.
From an empty directory, initialize a new Supabase project:
npx supabase initLink it to your Supabase project using your Project ID (found in Supabase Dashboard → Project Settings → General):
npx supabase link --project-ref your-project-idCreate a new Edge Function:
npx supabase functions new sahha-webhookReplace the contents of supabase/functions/sahha-webhook/index.ts with:
import { createClient } from "https://esm.sh/@supabase/supabase-js@2";
const SECRET = Deno.env.get("SAHHA_WEBHOOK_SECRET") ?? "";
const SUPABASE_URL = Deno.env.get("SUPABASE_URL") ?? "";
const SUPABASE_SERVICE_ROLE_KEY =
Deno.env.get("SUPABASE_SERVICE_ROLE_KEY") ?? "";
const encoder = new TextEncoder();
async function hmacSha256(
secret: string,
data: Uint8Array,
): Promise<string> {
const key = await crypto.subtle.importKey(
"raw",
encoder.encode(secret),
{ name: "HMAC", hash: "SHA-256" },
false,
["sign"],
);
const sig = await crypto.subtle.sign("HMAC", key, data);
return [...new Uint8Array(sig)]
.map((b) => b.toString(16).padStart(2, "0"))
.join("");
}
async function sha256Hex(data: Uint8Array): Promise<string> {
const hash = await crypto.subtle.digest("SHA-256", data);
return [...new Uint8Array(hash)]
.map((b) => b.toString(16).padStart(2, "0"))
.join("");
}
Deno.serve(async (req) => {
try {
const signature = (req.headers.get("x-signature") ?? "").trim();
const eventType = (req.headers.get("x-event-type") ?? "").trim();
const externalId = (req.headers.get("x-external-id") ?? "").trim();
if (!signature) {
return new Response("Missing X-Signature", { status: 400 });
}
const rawBody = new Uint8Array(await req.arrayBuffer());
if (!SECRET) {
return new Response("Missing SAHHA_WEBHOOK_SECRET", { status: 500 });
}
const computed = await hmacSha256(SECRET, rawBody);
if (computed !== signature) {
return new Response("Invalid signature", { status: 401 });
}
const payload = JSON.parse(new TextDecoder().decode(rawBody));
const eventHash = await sha256Hex(rawBody);
const supabase = createClient(SUPABASE_URL, SUPABASE_SERVICE_ROLE_KEY);
const { error } = await supabase.from("sahha_events").upsert(
{
event_type: eventType || "unknown",
external_id: externalId,
payload,
event_hash: eventHash,
},
{ onConflict: "event_hash" },
);
if (error) {
console.error("Insert error:", error);
return new Response("Database error", { status: 500 });
}
return new Response("ok", { status: 200 });
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
return new Response("Server error", { status: 500 });
}
});Create a migration file at supabase/migrations/001_create_sahha_events.sql:
create table if not exists sahha_events (
id bigint generated always as identity primary key,
event_type text not null,
external_id text not null default '',
payload jsonb not null default '{}',
event_hash text not null,
created_at timestamptz not null default now(),
constraint sahha_events_event_hash_unique unique (event_hash)
);
create index if not exists idx_sahha_events_event_type
on sahha_events (event_type);
create index if not exists idx_sahha_events_external_id
on sahha_events (external_id);Apply the migration:
npx supabase db pushWhen prompted, confirm with Y to apply the migration. You can verify the table was created in the Supabase Dashboard → Table Editor → sahha_events.
Deploy and connect to Sahha
Store your webhook secret
Sahha signs every webhook request. Your Edge Function must verify this signature.
- In Sahha, go to Data Delivery → Webhooks → Create webhook
- Copy the Secret value
Then in your terminal run:
npx supabase secrets set SAHHA_WEBHOOK_SECRET=your_secretReplace your_secret with the actual secret you copied from Sahha.
npx supabase secrets list — you should see SAHHA_WEBHOOK_SECRET in the output. You can also check in the Supabase Dashboard → Project Settings → Edge Functions → Secrets. Deploy the Edge Function
npx supabase functions deploy sahha-webhook --no-verify-jwtAfter deployment, use the Edge runtime URL as your webhook destination:
https://<project-ref>.functions.supabase.co/sahha-webhook<project-ref>.supabase.co/functions/v1/...) expects an Authorization header and is designed for your own app. For third-party webhooks like Sahha, use the Edge runtime URL (<project-ref>.functions.supabase.co/...) — it works cleanly without JWT auth and respects --no-verify-jwt. You can find your project ref in the Supabase Dashboard → Project Settings → General.

Configure Sahha
Go to Sahha Dashboard → Data Delivery → Webhooks → Create webhook and fill in:
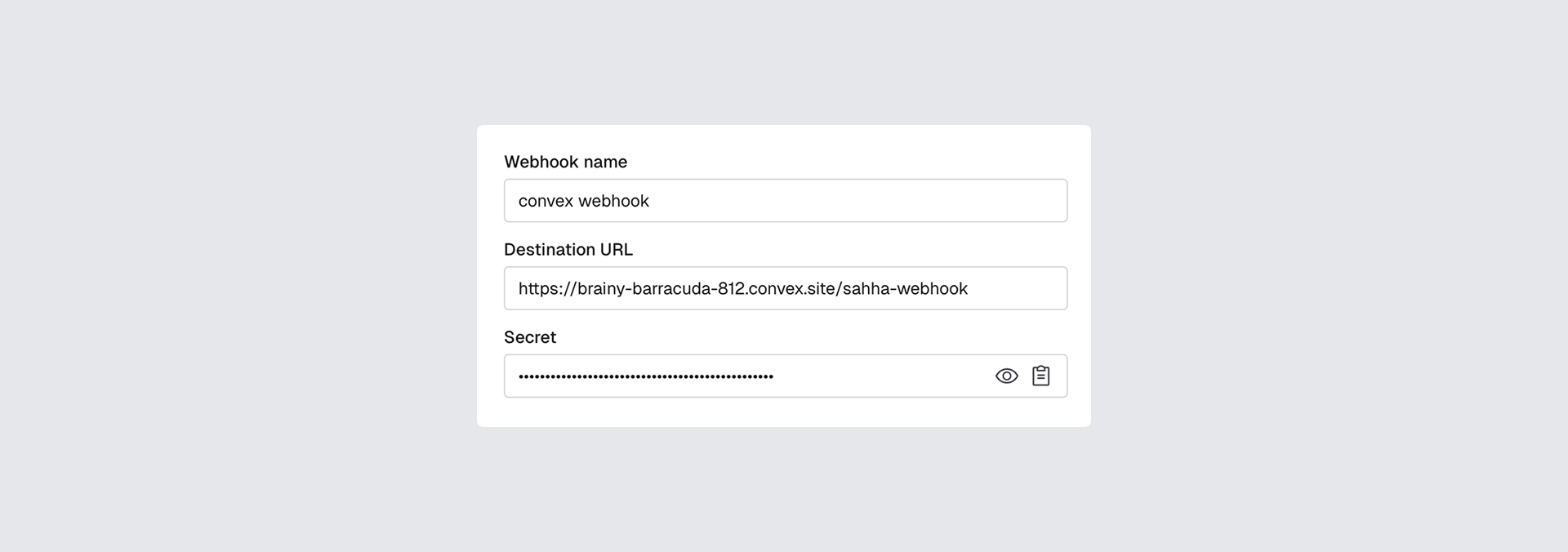
- Webhook name:
Supabase Webhook - Destination URL: your Edge Function URL from above
- Event subscriptions: choose the data you want to stream — Health Scores, Biomarkers, Archetypes, Raw Data Logs
Click Create webhook.
Test the webhook
In the Sahha dashboard, find your webhook and click Actions → Test. This sends a real signed test payload to your endpoint.
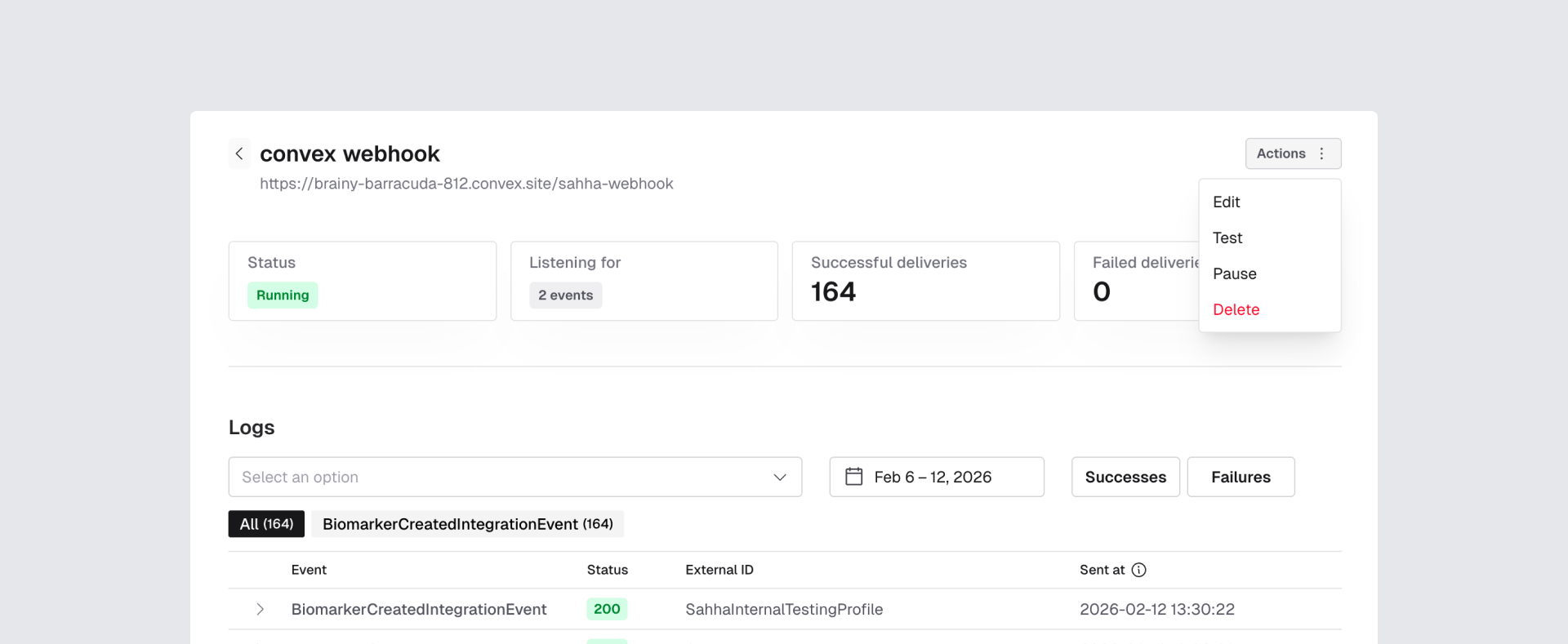
sahha-webhook → Logs — you should see a successful invocation. How data works in Supabase
Events are stored in the sahha_events table — a single flat Postgres table with deduplication built in via a unique constraint on event_hash.
Here’s an example of a biomarker event payload that Sahha sends via webhook:
{
"id": "1cb680dd-7e67-553c-9a29-c1bc066f6eb7",
"type": "activity_low_intensity_duration",
"unit": "minute",
"value": "345",
"version": 1,
"category": "activity",
"accountId": "4e9357a7-6275-4b22-b0f8-524962e4c7f7",
"profileId": "b27fac52-0ae6-49d5-97c4-d720b7d6be16",
"valueType": "long",
"externalId": "SahhaInternalTestingProfile",
"aggregation": "total",
"endDateTime": "2026-02-11T23:59:59Z",
"periodicity": "daily",
"createdAtUtc": "2026-02-11T04:00:22.724731Z",
"startDateTime": "2026-02-11T00:00:00Z"
}X-External-Id header with every webhook. Set this to your Supabase Auth UID when creating Sahha profiles so you can map events back to the correct user in your database. Troubleshooting
Webhook requests aren't reaching Supabase
Check:
- You deployed the function to the correct Supabase project (
npx supabase linkpointed to the right project) - You copied the correct Edge Function URL from the Supabase dashboard
- Your Sahha webhook Destination URL matches that exact URL
401 Invalid signature
This means your secret in Supabase does not match Sahha.
Fix:
npx supabase secrets set SAHHA_WEBHOOK_SECRET=your_secret
npx supabase functions deploy sahha-webhook --no-verify-jwtNo data in the database
- Confirm Sahha is actually receiving data (Demo App or SDK active)
- Check Edge Function logs in the Supabase Dashboard → Edge Functions →
sahha-webhook→ Logs - Verify the migration was applied: run
npx supabase db pushif you haven’t already
Next steps
You now have a secure, production-ready Sahha webhook endpoint in Supabase with automatic streaming into Postgres.